Understanding E. Coli: Detection, Transmission, Prevention, And Treatment
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a type of bacteria that can be found in the intestines of humans and animals. Most strains of E. coli are harmless, but some can cause serious infections, including food poisoning, urinary tract infections (UTIs), and sepsis.
Understanding E. coli: Everything you need to know about this serious - Source www.msn.com
Editor's Note:
Understanding E. coli: Detection, Transmission, Prevention, And Treatment has published on date. This topic is incredibly important to read to protect yourself and your loved ones from the harmful effects of E. coli.
We did some analysis, digging information, made Understanding E. coli: Detection, Transmission, Prevention, And Treatment we put together this Understanding E. coli: Detection, Transmission, Prevention, And Treatment guide to help target audience make the right decision.
Key Differences or Key Takeaways
| Characteristic | Harmless E. coli | Pathogenic E. coli |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Intestines of humans and animals | Intestines of humans and animals, can cause infection in other parts of the body |
| Symptoms | None | Diarrhea, vomiting, abdominal pain, fever, urinary tract pain, sepsis |
| Treatment | Not needed | Antibiotics, hospitalization |
Main Article Topics
- Detection of E. coli
- Transmission of E. coli
- Prevention of E. coli
- Treatment of E. coli
FAQ
This FAQ section provides comprehensive answers to frequently asked questions about Escherichia coli (E. coli), its detection, transmission, prevention, and treatment. Understanding E. coli: Detection, Transmission, Prevention, And Treatment
Understanding E. coli: causes, symptoms, and prevention - DFA - Source www.dfa.co.za
Question 1: What are the symptoms of E. coli infection?
E. coli infection can cause a range of symptoms, including severe abdominal cramps, diarrhea (often bloody), nausea, vomiting, fever, fatigue, and loss of appetite. In some cases, it can also lead to more serious complications, such as kidney failure, hemolytic uremic syndrome (HUS), and sepsis.
Question 2: How is E. coli detected?
E. coli is typically detected through laboratory testing of stool samples. The presence of certain strains of E. coli can be identified using specific diagnostic tests, such as polymerase chain reaction (PCR).
Question 3: How is E. coli transmitted?
E. coli is primarily transmitted through contaminated food or water. It can also be spread through contact with animals or their feces, or from person to person through poor hygiene practices.
Question 4: How can E. coli infection be prevented?
There are several ways to prevent E. coli infection, including: washing hands thoroughly with soap and water, especially after using the bathroom and before handling food; cooking meat thoroughly; avoiding raw or undercooked animal products; drinking clean water; and practicing good hygiene when caring for animals.
Question 5: What is the treatment for E. coli infection?
Treatment for E. coli infection typically involves supportive care, such as rehydration and pain medication. In severe cases, antibiotics may be prescribed. It is important to seek medical attention promptly if you suspect you have an E. coli infection.
Question 6: What are the long-term effects of E. coli infection?
In most cases, E. coli infection resolves without any long-term effects. However, in some cases, it can lead to complications such as kidney damage, HUS, or sepsis. Prompt treatment and follow-up care are essential to minimize the risk of long-term consequences.
By understanding the answers to these frequently asked questions, you can better protect yourself and others from E. coli infection.
For more comprehensive information on E. coli, refer to: Understanding E. coli: Detection, Transmission, Prevention, And Treatment
Tips
To minimize the risk of E. coli infection, consider the following practical tips:
Tip 1: Practice Thorough Hand Hygiene
Washing hands thoroughly with soap and water, particularly after using the bathroom, changing diapers, and handling animals, helps prevent the spread of E. coli. Avoid touching your mouth, nose, or eyes with unclean hands.
Tip 2: Cook Meat Properly
Thoroughly cooking meat, especially ground beef and poultry, to an internal temperature of 160°F (71°C) or higher ensures that any potential E. coli bacteria are killed.
Tip 3: Avoid Unpasteurized Milk and Juice
Unpasteurized milk and juice may contain harmful bacteria, including E. coli. Opting for pasteurized counterparts significantly reduces the risk of infection.
Tip 4: Clean and Disinfect Surfaces Regularly
Regularly cleaning and disinfecting surfaces that come into contact with food or are frequently touched, such as countertops, doorknobs, and refrigerator handles, helps minimize the spread of bacteria.
Tip 5: Wash Fruits and Vegetables Thoroughly
Rinse fruits and vegetables thoroughly under running water before consuming them to remove dirt, bacteria, and any potential E. coli. Peel fruits and vegetables whenever possible.
Tip 6: Avoid Cross-Contamination in the Kitchen
Use separate cutting boards and utensils for raw meat and other foods to prevent cross-contamination. Wash hands thoroughly after handling raw meat.
Tip 7: Maintain Proper Food Storage
Keep food at the appropriate temperatures to inhibit bacterial growth. Refrigerate perishable foods and freeze meat within two hours of purchasing to maintain food safety.
Tip 8: Seek Medical Attention Promptly
If you experience symptoms of an E. coli infection, such as severe diarrhea, abdominal pain, nausea, and vomiting, seek medical attention immediately. Prompt diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent complications.
By incorporating these tips into daily practices, you can significantly reduce the risk of E. coli infection and safeguard your health.
Understanding E. Coli: Detection, Transmission, Prevention, And Treatment
Escherichia coli (E. coli) is a crucial bacterium in our ecosystem, offering both benefits and health risks. A deeper understanding of E. coli is vital to mitigate its potential threats while harnessing its beneficial aspects. This comprehensive exploration delves into six key aspects: detection, transmission, prevention, and treatment, providing valuable insights into E. coli's role in our world.
- Microscopic Detection: Identifying E. coli's presence using specialized techniques.
- Fecal-Oral Transmission: Understanding the primary mode of E. coli transmission, often associated with contaminated food and water.
- Hygiene Practices: Emphasizing proper handwashing and sanitation to prevent E. coli infections.
- Antimicrobial Treatment: Exploring the use of antibiotics to combat certain E. coli strains causing disease.
- Beneficial Symbiosis: Recognizing E. coli's essential role in human digestion and vitamin synthesis.
- Pathogenic Strains: Differentiating between harmless E. coli strains and pathogenic ones responsible for severe infections.
These aspects underscore the importance of understanding E. coli's complex nature. Proactively detecting and preventing E. coli contamination is crucial for public health. Combining effective hygiene practices with targeted treatment approaches can significantly reduce the risk of infection. Furthermore, appreciating E. coli's beneficial contributions to our ecosystem highlights the need for a balanced perspective in managing its potential risks.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc()/e-coli-symptoms-diagnosis-treatment-4174407_FINAL-5bc3f6a2c9e77c0051aa3143.png)
Un aperçu d'E. Coli - Fmedic - Source fmedic.org
Understanding E. Coli: Detection, Transmission, Prevention, And Treatment
Understanding E. coli is essential for protecting public health. This bacterium can cause a variety of illnesses, including food poisoning, urinary tract infections, and sepsis. Early detection and treatment are essential for preventing serious complications. Understanding how E. coli is transmitted can help prevent its spread. Prevention measures include proper food handling and hygiene. Effective treatment involves antibiotics and supportive care. A comprehensive understanding of E. coli is crucial for safeguarding individuals and communities.
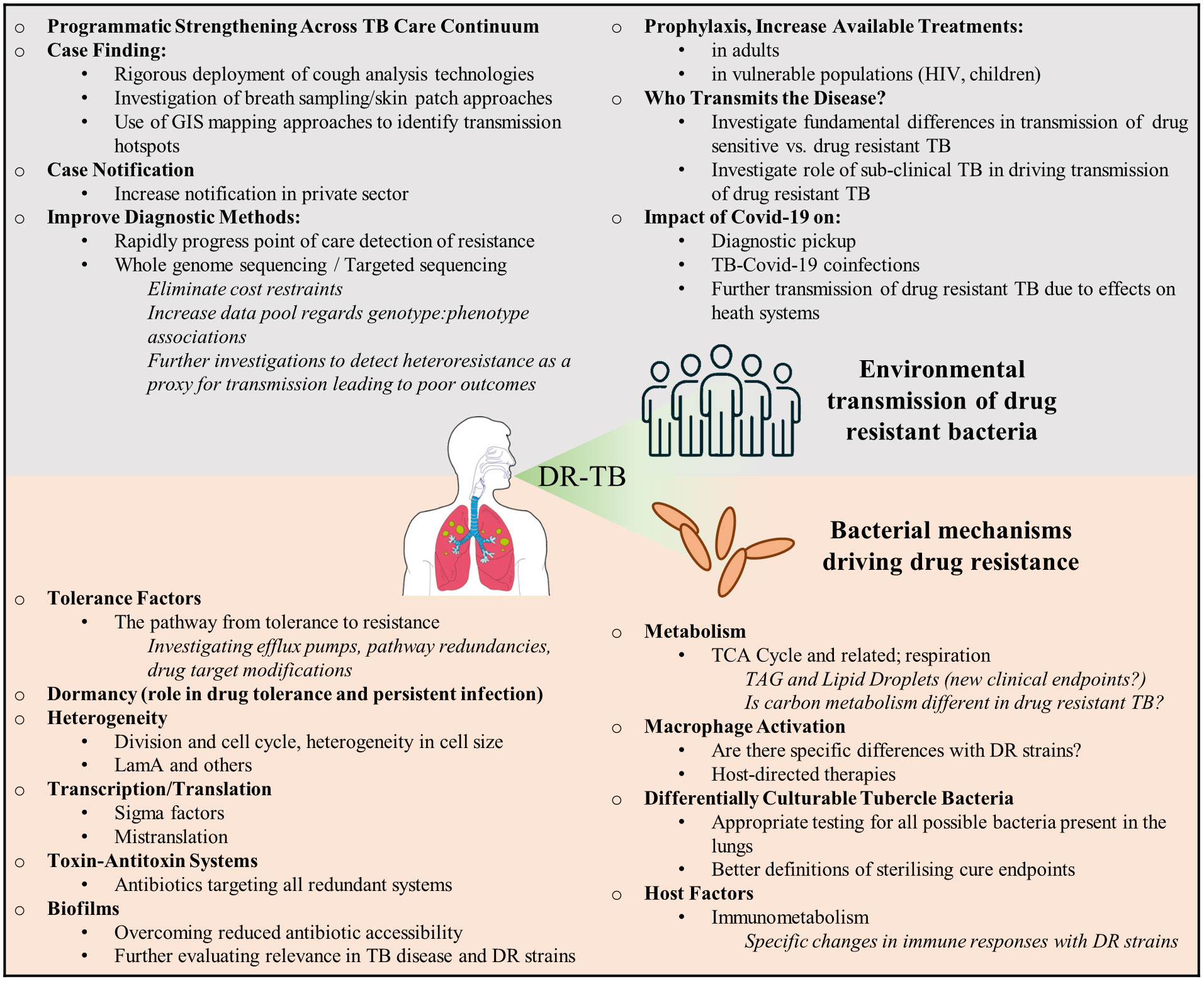
Frontiers | Drug resistant tuberculosis: Implications for transmission - Source www.frontiersin.org
Detection of E. coli is achieved through laboratory testing of stool, urine, or blood samples. This allows for the identification of the specific strain and determination of its antibiotic susceptibility. Understanding the transmission pathways of E. coli, such as contaminated food or water, aids in developing effective prevention strategies. Handwashing, proper food preparation, and sanitation practices are key in preventing its spread. Treatment typically involves antibiotics to eliminate the bacteria, along with supportive care measures like fluids and pain relievers. Antibiotic selection is guided by the E. coli strain's susceptibility profile, ensuring effective treatment.
The understanding of E. coli detection, transmission, prevention, and treatment empowers individuals and healthcare professionals to take proactive steps in safeguarding public health. Early detection and prompt treatment can significantly improve patient outcomes and prevent the spread of this potentially harmful bacterium. Continued research and surveillance efforts are vital for staying ahead of emerging strains and developing innovative prevention and treatment strategies.
Conclusion
Understanding E. coli: Detection, Transmission, Prevention, and Treatment provides critical knowledge for safeguarding public health. Early detection and prompt treatment are crucial for preventing serious complications. Understanding transmission pathways enables effective prevention measures. Proper food handling, hygiene, and sanitation practices are essential in preventing the spread of this bacterium.
Effective treatment involves antibiotics tailored to the specific E. coli strain. Continued research and surveillance are vital for staying ahead of emerging strains and developing innovative strategies. A comprehensive understanding of E. coli empowers individuals and healthcare professionals to protect themselves and their communities from this potentially harmful bacterium.
